Where did that payment go? Why doesn’t the ledger match the bank statement?
The numbers don’t lie—except when they do. One missing transaction, an unaccounted bank fee, or a misapplied payment can send your books into chaos. Accountants, bookkeepers, and financial controllers know the struggle: scanning spreadsheets, cross-checking bank statements, and manually tracking down discrepancies that refuse to resolve themselves. The bigger the business, the bigger the mess.
Without the right payment reconciliation software, financial accuracy becomes a guessing game. What’s the real cash balance? Are all transactions properly recorded? Where are the discrepancies hiding? Instead of firefighting month-end surprises, the best reconciliation tools automate matching, flag inconsistencies, and ensure real-time visibility—so you’re focused on strategic financial oversight, not drowning in data.
Let’s cover the top 10 payment reconciliation software providers that make financial clarity effortless, but first:
What is payment reconciliation software?
Payment reconciliation software is a specialized tool used by treasury and finance teams to match incoming and outgoing payments with corresponding invoices, bank statements, and accounting records. It automates the reconciliation process, reduces manual effort, improves accuracy, and ensures that financial records are up to date.
How it works
-
Data collection: The software gathers transaction data from multiple sources, such as bank statements, ERP systems, payment processors, and accounting platforms.
-
Matching transactions: It automatically compares payments with invoices, purchase orders, or ledger entries based on predefined rules (e.g., amount, reference number, date).
-
Identifying discrepancies: Any unmatched or inconsistent transactions are flagged for review. The software can suggest possible matches or highlight missing payments.
-
Exception handling: Treasury teams can investigate and resolve issues like overpayments, underpayments, duplicate transactions, or chargebacks.
-
Reporting & Compliance: Generates audit-ready reports, ensuring transparency and compliance with accounting standards and regulations.
Key features to look for in payment reconciliation software
- Automated matching: The ability to automatically match transactions from different sources (e.g., bank statements, payment gateways, accounting systems) to identify discrepancies quickly.
- Multi-currency support: Handling transactions in multiple currencies is crucial for businesses operating internationally.
- Real-time data integration: Seamless integration with various financial systems and real-time data updates to ensure accuracy and timeliness.
- Customizable rules and workflows: Flexibility to set up custom matching rules and workflows to suit specific business needs and processes.
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics: Detailed reports and analytics to provide insights into reconciliation processes, identify trends, and support decision-making.
- User-friendly interface: An intuitive and easy-to-use interface to minimize the learning curve and improve efficiency.
- Audit trail: Maintaining a detailed audit trail of all reconciliation activities for transparency and accountability.
- Customer support: Reliable customer support to assist with any issues or questions that may arise.
Evaluation criteria for reconciliation software
- Accuracy and reliability: The software should accurately match transactions and reliably identify discrepancies.
- Ease of use: The user interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate, reducing the learning curve for new users.
- Integration capabilities: The ability to integrate seamlessly with your existing financial systems, such as ERP, accounting software, and payment gateways.
- Automation: The extent to which the software can automate the reconciliation process, including transaction matching and exception handling.
- Customization: The ability to customize rules, workflows, and reports to fit your specific business processes and requirements.
- Scalability: The software should be able to handle increasing transaction volumes as your business grows.
- Security: Robust security features to protect sensitive financial data, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Reporting and analytics: Comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities to provide insights into reconciliation processes and support decision-making.
- Support and training: Availability of customer support and training resources to help users get the most out of the software.
- Cost: The total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance and support.
- Audit trail: The ability to maintain a detailed audit trail of all reconciliation activities for transparency and accountability.
- Performance: The software's performance in terms of speed and efficiency, especially when handling large volumes of transactions.
Best payment reconciliation software providers
- Nomentia: A comprehensive cash and treasury management solution that automates payment reconciliation across multiple banks and ERPs.
- Zoho: A user-friendly accounting platform with automated bank reconciliation and seamless integration with other Zoho apps.
- Zarmoney: An affordable accounting software with built-in reconciliation tools for matching payments with invoices and bank statements.
- Xero: A cloud-based accounting solution offering automated bank feeds, transaction matching, and robust financial reporting.
- QuickBooks: A widely-used accounting software with smart reconciliation features and strong integration with banking and financial tools.
- Sage: A scalable accounting and financial management system with automation-driven reconciliation and compliance features.
- Upflow: A cash flow management platform that streamlines payment reconciliation while improving receivables tracking.
- FloQast: A close management software that enhances financial reconciliation with automation, collaboration, and audit-ready workflows.
- BlackLine: An enterprise-grade financial automation solution specializing in high-volume reconciliation, reporting, and fraud prevention.
- SAP: A powerful ERP solution with integrated reconciliation capabilities designed for large enterprises managing complex financial operations.
Top 10 cash flow forecasting solutions: Key features, strengths & best for
1. Nomentia
Nomentia offers a comprehensive suite of cash and treasury management solutions, including payment reconciliation. It centralizes and automates the reconciliation process by matching bank statements with transaction data and posting them to the general ledger or accounting software.
Nomentia’s SaaS solution also offers solutions for payment automation, payment fraud & error prevention, liquidity management, cash flow forecasting, predictive analytics, cash visibility, bank account management, bank connectivity management, trade finance, in-house banking, risk management, FX risk, and treasury workflows and reporting.
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated transaction matching, multi-currency support, real-time data integration, customizable workflows | Strong integration capabilities, robust security features, scalable for growing businesses and cash management complexity. | May require training for new users, higher cost for advanced features | Large-to-mid-size enterprises and multinational corporations |
2. Zoho
Zoho offers a business software suite, including Zoho Books for accounting and reconciliation. It automates payment matching with invoices, provides customizable matching rules, and includes a bank reconciliation tool to align records with bank statements.
Source: zoho.com
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated transaction matching, multi-currency support, real-time data integration, customizable workflows | Strong integration capabilities, robust security features, scalable for growing businesses and cash management complexity. | May require training for new users, higher cost for advanced features | Large-to-mid-size enterprises and multinational corporations |
3. Zarmoney
Zarmoney is an accounting software that simplifies payment reconciliation by matching payments with invoices and bank accounts. It provides real-time updates and alerts for discrepancies to help businesses maintain accurate financial records.
Source: zarmoney.com
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated transaction matching, customizable invoices, real-time financial reporting, multi-currency support | Easy to use, affordable pricing, good customer support | Limited integration options, basic reporting features | Small businesses and startups. |
4. Xero
Xero, is a cloud-based accounting software with built-in reconciliation tools. It automatically matches payments with invoices, allows users to set custom matching rules, and provides alerts for discrepancies.
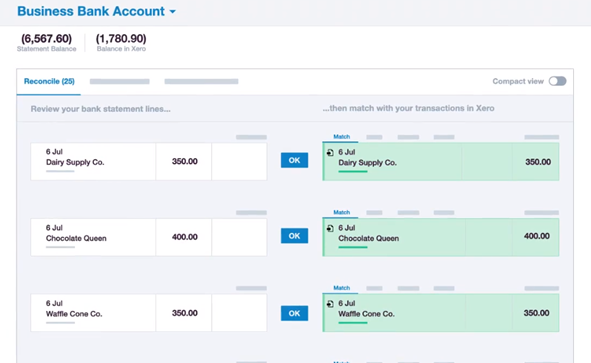
Source: xero.com
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated bank feeds, multi-currency support, customizable reports, integration with over 800 apps | Intuitive interface, strong integration capabilities, excellent customer support | Higher cost for premium plans, limited offline functionality | Small to medium-sized businesses |
5. Quickbooks
Quickbooks is a widely used accounting solution with robust reconciliation features. It automates payment matching with invoices and includes a bank reconciliation tool to ensure records align with bank statements.
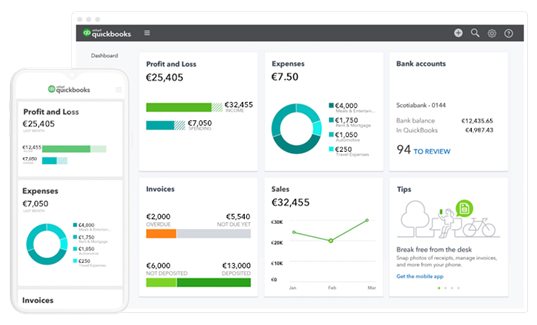
Source: quickbooks.com
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated bank feeds, multi-currency support, customizable reports, integration with financial apps | User-friendly interface, strong customer support, scalable for growing businesses | Higher cost for advanced features, occasional performance issues | Small to medium-sized businesses |
6. Sage
Sage provides accounting and financial management tools, including payment reconciliation. It enables businesses to match payments with invoices, reconcile accounts, and stay compliant with financial regulations.
Source: sage.com
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated transaction matching, multi-currency support, customizable reports, integration with Sage products | Strong integration capabilities, robust security features, scalable for growing businesses | Higher cost for advanced features, may require training for new users | Medium to large-sized businesses |
7. Upflow
Upflow is a cash flow management platform with reconciliation features. It helps businesses automate payment matching, reconcile accounts, and provides real-time updates on cash flow discrepancies.
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated transaction matching, real-time cash flow insights, customizable reports, accounting software integration | User-friendly interface, strong customer support, affordable pricing | Limited advanced features, may not scale well for very large businesses | Small to medium-sized businesses |
8. Floqast
Floqast is a close management software with reconciliation capabilities. It supports payment matching, account reconciliation, and provides audit-ready financial processes.
Source: floqast.com
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated transaction matching, real-time collaboration tools, customizable workflows, ERP integration | Strong integration capabilities, robust reporting features, excellent customer support | Higher cost for advanced features, may require training for new users | Medium to large-sized businesses |
9. Blackline
Blackline is a financial close and reconciliation software that automates transaction matching and discrepancy alerts. It helps businesses streamline financial processes and reduce errors.
Source: blackline.com
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated transaction matching, real-time data integration, customizable workflows, comprehensive reporting | Strong integration capabilities, robust security features, scalable for growing businesses | May require training for new users, higher cost for advanced features | Large-to-mid-size enterprises and multinational corporations |
10. SAP
SAP provides an enterprise-grade reconciliation solution integrated into its ERP suite. It allows businesses to match payments with invoices, reconcile accounts, and align records with bank statements.
| Key features | Pros | Considerations | Best suited for |
| Automated transaction matching, multi-currency support, real-time data integration, customizable workflows | Strong integration capabilities for SAP users, robust security features, scalable for growing businesses | Higher cost for advanced features, may require training for new users | Large enterprises and multinational corporations |
How to choose the right payment reconciliation software for your business?
- Assess your business needs
- Identify specific pain points in your current reconciliation process (e.g., manual data entry, inefficiencies, lack of integration).
- Define key requirements, such as multi-currency support, automation, integration with existing financial systems, and security needs.
- Research available options
- Create a shortlist of software solutions that align with your business needs.
- Read user reviews and case studies to understand real-world experiences and potential challenges.
- Evaluate key features
- Look for automation capabilities to reduce manual work and improve efficiency.
- Ensure seamless integration with your ERP, banking systems, and accounting software.
- Assess customization options for workflows, reporting, and reconciliation rules.
- Verify security features to protect financial data from fraud and errors.
- Consider business scope and geographic footprint
- Choose a solution that supports your business structure (e.g., single-entity vs. multi-entity reconciliation).
- Ensure multi-currency and cross-border transaction support if operating in multiple regions.
- Analyze usability and support
- Evaluate the user interface for intuitiveness and ease of adoption.
- Check for available training resources and customer support to facilitate implementation and troubleshooting.
- Assess costs and ROI
- Consider the total cost of ownership, including software licenses, implementation, and ongoing maintenance.
- Weigh potential ROI by measuring efficiency gains, error reduction, and compliance improvements.
- Plan for implementation
- Develop an implementation roadmap, including setup, data migration, and training schedules.
- Assign responsibilities and set milestones to ensure a smooth transition.
- Monitor performance and optimize
- Track system performance and user feedback after implementation.
- Adjust and optimizations to ensure continuous improvement in reconciliation efficiency.
Final thoughts: The right payment reconciliation software changes everything
Manual reconciliation is a time sink, riddled with inefficiencies, errors, and unnecessary stress. The right software does a lot more than just match transactions; it transforms financial management by providing real-time accuracy, reducing fraud risks, and freeing up valuable time for strategic decision-making.
Whether you're a small business looking for a simple solution or a multinational enterprise needing advanced automation and integration, there’s a reconciliation tool designed for you. By choosing the right provider, you ensure financial clarity, streamline operations, and gain control over your cash flow—so reconciliation becomes a seamless process, not a monthly nightmare.



